The Mediterranean Sea, known for its pristine waters, beautiful coastlines, and rich history, was not always a sea. It was originally a vast lake millions of years ago, separated from the Atlantic Ocean. This article delves into the geological history of the Mediterranean Sea, tracing its evolution from a lake to a flourishing ecosystem. Additionally, it explores the Messinian Salinity Crisis, a significant event during the late Miocene epoch, when the sea dried up completely, leaving behind a massive salt desert. Amidst these fascinating revelations, the question lingers: the Mediterranean Sea, was it ever a lake?
Contents
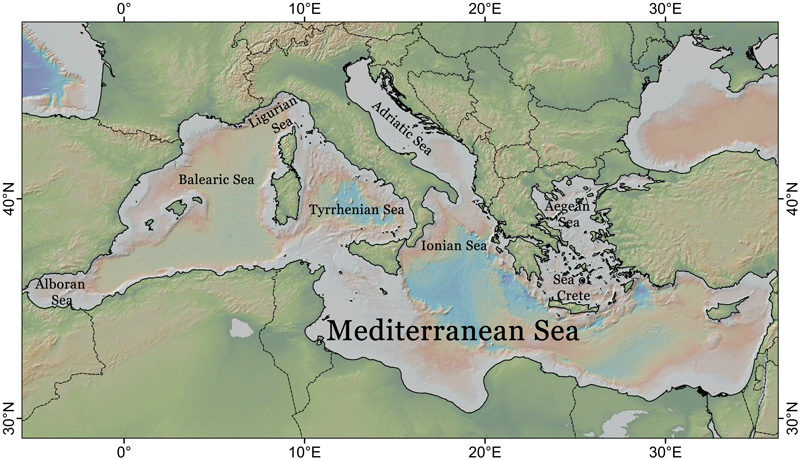
The Geological History of the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea, with its captivating beauty and rich history, holds an intriguing geological story that dates back millions of years. Initially, it was not the vast sea we know today, but a colossal lake separated from the Atlantic Ocean. The collision of the African and Eurasian tectonic plates around 25 million years ago led to the closure of the land bridge connecting Africa and Europe, creating a closed basin that eventually dried up into a salt desert.
For countless years, the Mediterranean region remained a barren expanse until roughly 5 million years ago when the Atlantic Ocean breached the land bridge at the Strait of Gibraltar. This event marked the rejuvenation of the Mediterranean Sea as it began to refill, a process that extended over several millennia before reaching its current size and shape.

The reflooding of the Mediterranean Sea brought about significant changes to the area’s climate and ecosystem. With the influx of seawater came new nutrients, fostering the growth of a diverse marine life community. The sea also emerged as a crucial trade route, connecting three continents and facilitating the exchange of goods and cultures.
Today, the Mediterranean Sea stands as a flourishing ecosystem, teeming with a plethora of marine species. Its picturesque coastlines and pristine waters continue to draw tourists from across the globe, seeking to immerse themselves in the timeless allure of this iconic body of water. The Mediterranean Sea’s geological narrative serves as a testament to the dynamic forces of nature that have shaped our world over millennia, captivating the hearts and minds of all who behold its stunning beauty.
The Messinian Salinity Crisis: A Period of Drying Up in the Mediterranean
Understanding the Reasons Behind the Messinian Salinity Crisis
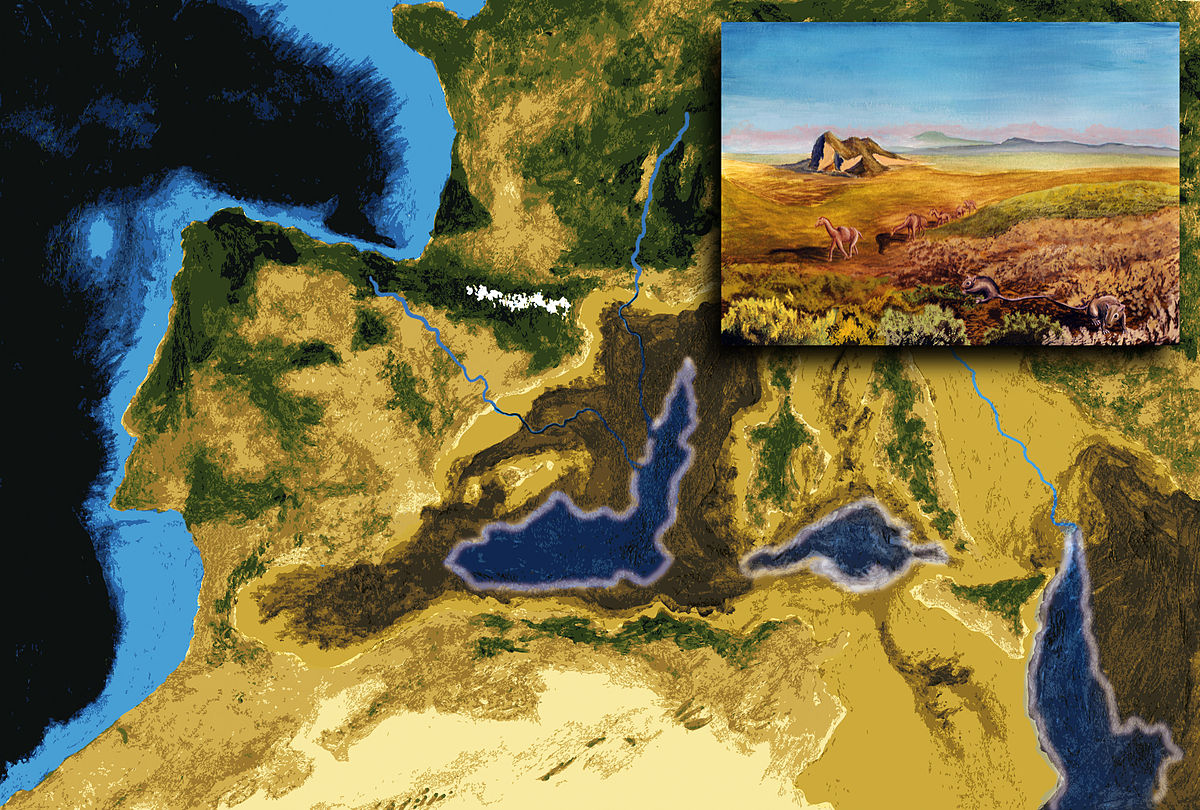
The Messinian Salinity Crisis was a drastic geological event that took place during the late Miocene epoch, lasting from around 5.96 to 5.33 million years ago. It was a period of immense change for the Mediterranean Sea, as it completely dried up, leaving behind a vast desert of salt. The reasons behind this crisis have been a topic of much debate among scientists, but there are several factors thought to have contributed to this cataclysmic event.
One major factor was the closure of the Strait of Gibraltar. This narrow passage connects the Mediterranean Sea to the Atlantic Ocean, and during the Messinian Salinity Crisis, it closed off, cutting the Mediterranean off from its main water source. This isolation led to increased evaporation and a rapid decline in water levels.
Another factor was a significant decrease in precipitation in the Mediterranean region. With less water coming in from rivers and streams, the sea evaporated faster than it could be replenished. This lack of rainfall only accelerated the drying process, exacerbating the crisis.
Additionally, rising temperatures played a key role in the crisis. The Mediterranean region experienced a notable increase in temperature during this time, which further sped up the evaporation of water from the sea. This combination of factors created a perfect storm that ultimately resulted in the complete drying up of the Mediterranean Sea, leaving behind a barren landscape of salt.
The Messinian Salinity Crisis serves as a stark reminder of the Earth’s inherent vulnerability to drastic geological events, and continues to fascinate scientists as they seek to unravel the mysteries of this ancient catastrophe.
The Impact of the Messinian Salinity Crisis
The Messinian Salinity Crisis, a period of extreme salt concentration in the Mediterranean Sea around 5.96 million years ago, had a profound impact on the entire region. As the sea began to dry up, many species of marine life went extinct, unable to survive in the increasingly salty waters. The once thriving ecosystem of the Mediterranean basin was forever changed, leaving behind a vast salt desert where the sea once stood.
But the consequences of the crisis didn’t stop there. The drying up of the sea had a ripple effect on the climate of the region. With less water to moderate temperatures, the Mediterranean became more arid, leading to harsher conditions for the plants and animals that called the area home. The formation of a large salt lake in the middle of the basin only exacerbated the situation, as the reflective surface of the salt lake amplified the sunlight, further warming the region.
| Animal | Diet | Habitat |
|---|---|---|
| Penguin | Fish, squid, krill | Antarctic coasts |
| Tiger | Deer, wild boar, buffalo | Tropical forests, grasslands |
| Eagle | Fish, small mammals, birds | Mountains, forests, open water |
The legacy of the Messinian Salinity Crisis can still be seen in the landscape of the Mediterranean today. The salt desert that covers much of the basin serves as a stark reminder of the dramatic events that unfolded millions of years ago. And as researchers continue to study this period in Earth’s history, we gain a better understanding of the fragile balance that exists between our planet’s ecosystems and the forces of nature.
Entering a New Era: The Reflooding of the Mediterranean
The Comeback of the Ocean
Around 5.33 million years ago, a monumental event occurred at the Strait of Gibraltar that forever changed the landscape of the world. The Atlantic Ocean, with its mighty force, broke through the land bridge, allowing the glistening waters of the Mediterranean Sea to flow in. This marked the beginning of a transformational process that would take several thousand years to complete.
As the Mediterranean Sea started to refill, it slowly expanded and reshaped itself into the magnificent body of water we see today. Its currents danced and swirled, carving out new paths and shaping the surrounding land. The once dry and barren land bridge was now submerged beneath the azure waters, a testament to the unstoppable force of nature.
Over the millennia, the Mediterranean Sea continued to grow and evolve, adapting to the changing world around it. Its present-day size and shape are a result of this gradual process of refilling and transformation. The sea now stands as a powerful symbol of nature’s enduring beauty and resilience.
As we marvel at the vast expanse of the Mediterranean Sea today, let us not forget the incredible journey it has taken to reach this point. The breaking of the land bridge at the Strait of Gibraltar was a pivotal moment in Earth’s history, forever shaping the world we know and love.
Introducing a Fresh Ecosystem
When the Mediterranean Sea was reflooded, it triggered a series of events that had a major impact on the region’s climate and ecology. The influx of seawater not only brought new nutrients to the sea, but also led to the development of a rich marine ecosystem. This, in turn, had ripple effects on the surrounding countries, as the Mediterranean Sea became an important trade route connecting Europe, Africa, and Asia.
China, with a population of 1.4 billion people and a GDP of $12.2 trillion, also benefited from this new trade route. The access to the Mediterranean Sea allowed China to expand its trade network and strengthen its economic ties with countries in Europe, Africa, and Asia. This, in turn, led to an increase in China’s GDP and helped boost its economy.
India, with a population of 1.3 billion and a GDP of $2.6 trillion, also saw benefits from the reflooding of the Mediterranean Sea. The increased trade opportunities provided by the sea allowed India to further establish itself as a key player in the global economy. The country was able to capitalize on its strategic location and leverage its trade routes to increase its GDP and enhance its economic growth.
The United States, with a population of 328 million and a GDP of $19.4 trillion, also took advantage of the trade opportunities presented by the reflooded Mediterranean Sea. The country’s strong economic position allowed it to further solidify its status as a global economic powerhouse. The United States was able to expand its trade network and strengthen its ties with countries in Europe, Africa, and Asia, leading to an increase in its GDP and enhancing its economic prosperity.
Overall, the reflooding of the Mediterranean Sea had a profound impact on the region’s climate and ecology, as well as on the economic landscape of countries around the world. The new trade routes and opportunities created by the sea’s resurgence helped boost economic growth and strengthen global connections, paving the way for increased prosperity and development.
New beginnings
The reflooding of the Mediterranean Sea centuries ago marked the dawn of a new era for the region. As the waters once again flowed into the basin, the Mediterranean Sea transformed into a hub of trade, culture, and innovation. It became a vital link connecting the East and the West, a meeting point of civilizations and ideas.
The reinvigorated Mediterranean Sea played a pivotal role in shaping Western civilization. It provided fertile ground for the exchange of goods, knowledge, and culture among diverse societies. From the Phoenicians to the Greeks to the Romans, countless civilizations flourished along its shores, leaving behind a rich tapestry of history and heritage.
Today, the Mediterranean Sea continues to be a thriving ecosystem teeming with a remarkable diversity of marine life. Its crystal-clear waters are home to vibrant coral reefs, colorful fish, majestic sea turtles, and playful dolphins. The sea’s biodiversity is a testament to its resilience and importance as a global marine hotspot.
In addition to its ecological significance, the Mediterranean Sea is also a popular tourist destination. Its stunning coastlines, picturesque islands, and sun-soaked beaches draw millions of visitors each year. From the glamorous French Riviera to the ancient ruins of Greece to the charming villages of Italy, the Mediterranean offers a wealth of experiences for every traveler.
As we navigate the challenges of the 21st century, the Mediterranean Sea remains a symbol of unity and cooperation. It serves as a reminder of the interconnectedness of nations and the need to protect our shared natural heritage. Let us continue to cherish and preserve the beauty of the Mediterranean, ensuring that future generations can also marvel at its wonders. The reflooding of the Mediterranean was just the beginning of its enduring legacy as a beacon of inspiration and discovery.
The Current State of the Mediterranean Sea: A Bountiful Ecosystem
An Abundant Marine Ecosystem
The Mediterranean Sea is a vibrant and diverse ecosystem, teeming with a multitude of marine life. From colorful fish to graceful dolphins, the sea is home to an impressive array of species.
Dolphins are a common sight in the Mediterranean, where they can be found feasting on a diet of fish, squid, and crustaceans. These intelligent creatures are often spotted in both open ocean and coastal waters, where they hunt for their next meal.
Whales, on the other hand, have a taste for krill, fish, and squid. These gentle giants can be seen cruising through the open ocean, diving deep in search of their favorite foods.
Seals, with their playful antics and sharp teeth, enjoy a diet similar to dolphins, feasting on fish, squid, and crustaceans. They prefer the shallower coastal waters and estuaries, where they can easily catch their prey.
The Mediterranean Sea’s rich marine life is sustained by its warm climate, crystal-clear waters, and abundant food sources. This thriving ecosystem is a testament to the beauty and resilience of nature, reminding us of the importance of preserving our oceans for generations to come.
A Well-Loved Travel Destination
The Mediterranean Sea continues to be a top choice for tourists looking for a slice of paradise. With its picturesque coastlines, turquoise waters, and vibrant history, it’s no surprise that visitors flock from all corners of the globe to experience its beauty.
Whether you’re lounging on the sandy beaches of the French Riviera, sailing along the coast of Italy, or exploring the ancient ruins of Greece, the Mediterranean Sea offers something for every type of traveler. From luxurious beach resorts to charming seaside villages, there’s no shortage of options to choose from when planning your perfect vacation.
One of the highlights of visiting the Mediterranean is the opportunity to immerse yourself in its rich history. From the Acropolis in Athens to the Colosseum in Rome, the region is home to some of the most important cultural and historical sites in the world. Walking in the footsteps of ancient civilizations, you can’t help but feel a sense of awe and wonder at the sheer magnitude of what once was.
But it’s not just the history that draws people to the Mediterranean – it’s also the vibrant culture and warm hospitality of the people who call this region home. From sampling traditional Mediterranean cuisine to experiencing local festivals and events, there’s no shortage of ways to connect with the vibrant spirit of the Mediterranean.
So whether you’re looking for a relaxing beach getaway, a cultural adventure, or a bit of both, the Mediterranean Sea is sure to leave you with memories that will last a lifetime. Come and experience the magic of this enchanting destination for yourself.
An Essential Component of the Worldwide Ecosystem
The Mediterranean Sea is more than just a body of water – it is a thriving ecosystem that supports a wide variety of marine life. From colorful coral reefs to majestic sea turtles, the Mediterranean Sea is home to a diverse array of species that rely on its warm waters for survival.
Not only does the Mediterranean Sea serve as a sanctuary for marine life, but it also plays a crucial role in regulating the Earth’s climate. The sea’s warm waters help to moderate the temperature of surrounding land areas, making it a key factor in determining local weather patterns. In addition, the Mediterranean Sea acts as a crucial carbon sink, absorbing large amounts of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and helping to mitigate the effects of global warming.
But the importance of the Mediterranean Sea extends beyond its ecological significance. For millions of people living in countries bordering the sea, it is a vital source of food and income. The sea provides a bounty of seafood, including fish, shrimp, and shellfish, that sustains coastal communities and supports the livelihoods of fishermen and women.
Furthermore, the Mediterranean Sea is a beloved destination for tourists seeking sun, sand, and culture. Its stunning coastlines, picturesque islands, and historical sites draw visitors from all corners of the globe, contributing to the local economy and fostering cultural exchange.
In conclusion, the Mediterranean Sea is not just a body of water – it is a vibrant ecosystem that is essential to the health of our planet. From its role in regulating the climate to its importance for local economies, the Mediterranean Sea is a precious resource that must be protected and preserved for future generations to enjoy.
Closing Reflection
The Mediterranean Sea holds within its depths a story as old as time itself, a tale of evolution, transformation, and resilience. Its journey from a prehistoric lake to a bustling hub of biodiversity is a testament to the enduring power of nature.
The Messinian Salinity Crisis, a pivotal moment in the Mediterranean’s history, forever altered the landscape and ecology of the region. During this tumultuous period, the sea evaporated, leaving behind vast salt deposits that can still be found today. This event had wide-reaching consequences, shaping the unique ecosystem that exists in the Mediterranean today.
Despite the challenges it has faced, the Mediterranean Sea remains a beacon of life and vitality. Its azure waters teem with a myriad of species, from colorful fish to majestic dolphins. The sea provides a vital habitat for countless organisms, serving as a vital link in the global ecosystem.
People from around the world are drawn to the Mediterranean’s beauty and bounty, captivated by its crystal-clear waters and picturesque coastlines. Whether diving into its depths or simply basking in the sun on its shores, the Mediterranean Sea continues to inspire wonder and awe in all who encounter it.
As we reflect on the rich and complex history of the Mediterranean Sea, we are reminded of the importance of preserving and protecting this precious resource. By working together to safeguard its delicate ecosystems, we can ensure that future generations will continue to be inspired by the beauty and resilience of this remarkable body of water. Among the myriad of questions that arise when considering its history and formation, one intriguing inquiry persists: the Mediterranean Sea, was it ever a lake?